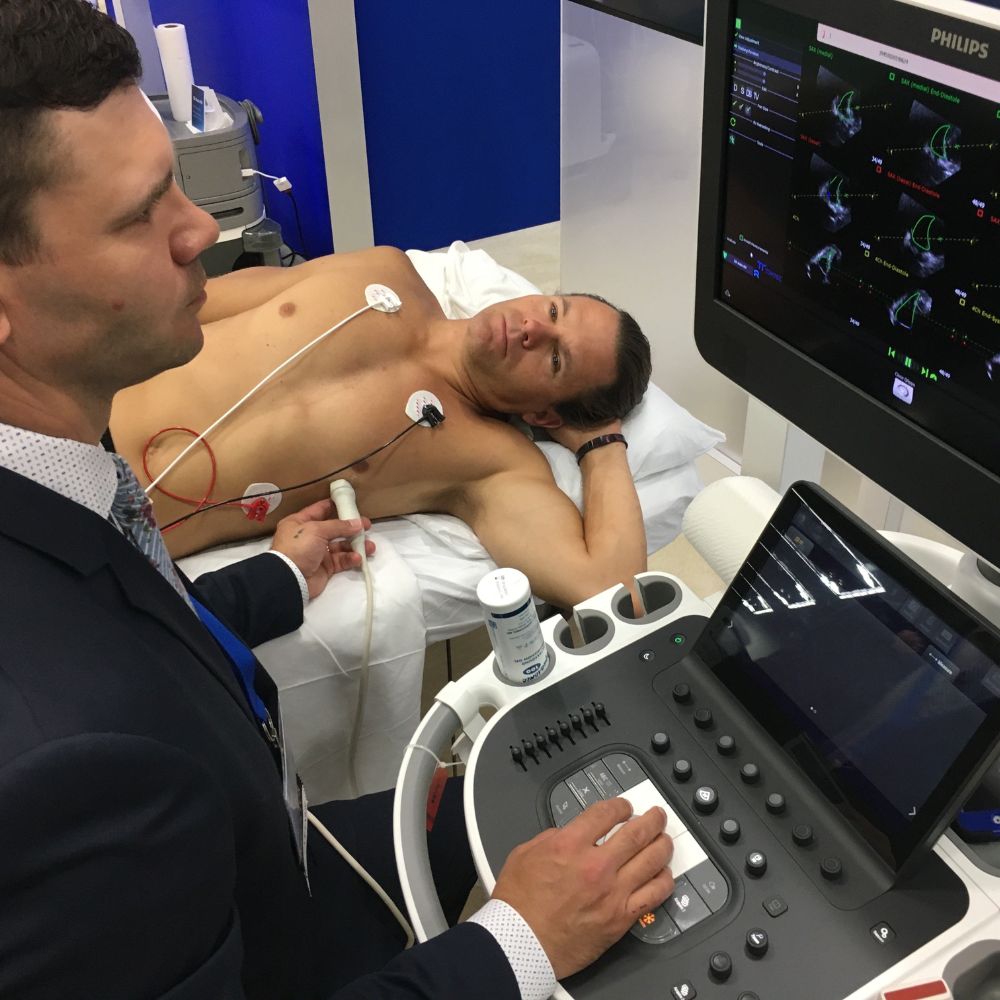
Digital Ultrasound Machine
An ultrasound machine takes internal images of deeper soft tissues by placing its probe on the skin surface. Ultrasonic sound waves traverse through the skin and underlying tissue image is formed on the monitor of machine which can be produced in the form of a picture for reporting.
An ultrasound scan uses high-frequency sound waves to make an image of a person’s internal body structures. Doctors commonly use ultrasound to study a developing fetus (unborn baby), a person’s abdominal and pelvic organs, muscles and tendons, or their heart and blood vessels.
Digital Ultrasound waves are transmitted from the transducer through the gel into the body. These short bursts of sound energy hit the desired organs and return to the probe as an echo. The probe diverts them to a bio meter present in the system. The bio meter converts the sound wave data into organ images.