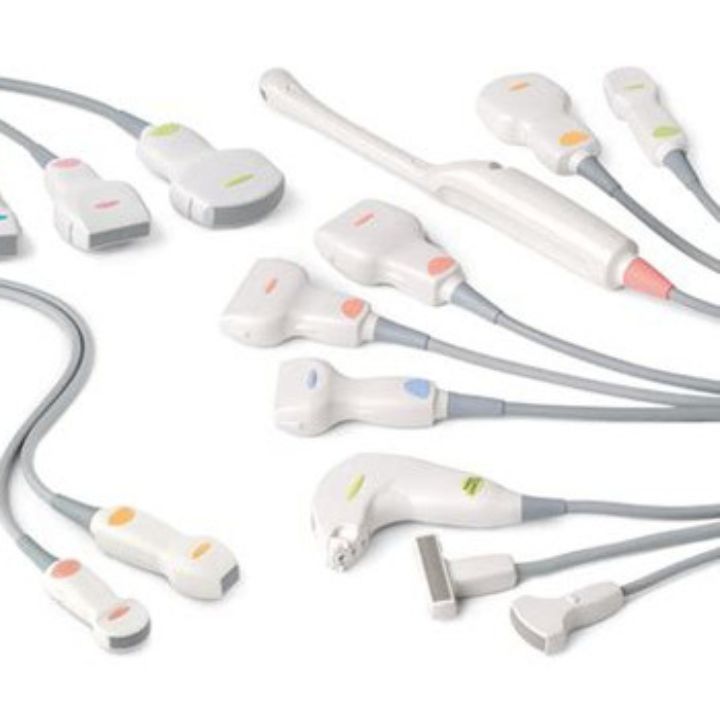
Ultrasound Probes
- Abdominal Imaging: Convex or curvilinear probes are commonly used for abdominal ultrasounds. They allow healthcare providers to assess organs like the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and gallbladder. The broad, curved design of these probes enables a comprehensive view of these internal structures.
- Obstetric and Gynecological Examinations: Trans vaginal and trans abdominal probes are utilized during pregnancy monitoring and gynecological assessments. These probes are designed with a slim, elongated shape for comfortable insertion and provide detailed images of the developing fetus, uterus, and ovaries.
- Cardiac Imaging: Phased-array probes are indispensable in cardiology. They are used for echocardiograms, which provide real-time images of the heart’s structure and function. The ability to adjust the direction and depth of the ultrasound beam is critical for assessing the heart’s various chambers and valves.
- Vascular Studies: Doppler ultrasound probes are essential for examining blood flow within veins and arteries. They can help diagnose conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and assess blood circulation in various parts of the body.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: High-frequency linear probes are employed for musculoskeletal ultrasound. They help visualize tendons, ligaments, and joints, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like tendonitis and ligament injuries.
- Breast Imaging: Specialized probes are designed for breast ultrasounds. These probes offer high-resolution imaging and are particularly useful for distinguishing between cysts and solid masses in breast tissue.
- Thyroid and Neck Examinations: Linear or high-frequency probes can be used for thyroid and neck ultrasounds. These examinations help assess thyroid nodules, lymph nodes, and other structures in the neck region.
- Prostate Imaging: Endo rectal or trans rectal probes are used for prostate ultrasounds. These probes are inserted into the rectum to obtain detailed images of the prostate gland and assist in diagnosing conditions like prostate cancer.